FACILITIES
Phaco Machine (Phacoemulsifer)
Phacoemulsification is a modern cataract surgery in which the eye’s internal lens is emulsified with an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye. Aspirated fluids are replaced with irrigation of balanced salt solution to maintain the anterior chamber.
Modern cataract surgery is made possible by the use of a complex machine called a phacoemulsifier, which breaks the cataract into tiny pieces and then suctions those pieces from the eye through a very small incision. Prior to the development of the phaco machine, the cataract was normally removed in one piece, requiring a larger incision, sutures, and more trauma to the eye. The phacoemulsification procedure is also faster, usually requiring less than 15 minutes per eye.

Pachymetry
A pachymeter is a medical device used to measure the thickness of the eye’s cornea. It is used to perform corneal pachymetry prior to LASIK surgery, for Keratoconus screening, LRI surgery and is useful in screening for patients suspected of developing glaucoma among other uses.
NCT Noncontact Tonometry (Pneumotonometry)
Noncontact (or air-puff) tonometry does not touch your eye but uses a puff of air to flatten your cornea. This type of tonometry is not the best way to measure intraocular pressure. But it is often used as a simple way to check for high IOP and is the easiest way to test children. This type of tonometry does not use numbing eyedrops.
Perimetry
Perimetry is the systematic measurement of visual field function. The two most commonly used types of perimetry are Goldmann kinetic perimetry and threshold static automated perimetry. With Goldmann or “kinetic” perimetry, a trained perimetrist moves the stimulus; stimulus brightness is held constant.
Fundus Camera
A fundus camera is a specialized low power microscope with an attached camera. Its optical design is based on the indirect ophthalmoscope. Fundus cameras are described by the angle of view – the optical angle of acceptance of the lens.
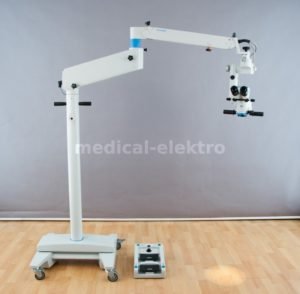
Operating Microscope
An operating microscope is an optical microscope specifically designed to be used in a surgical setting, typically to perform microsurgery.
Design features of an operating microscope are: magnification typically in the range from 4x-40x, components that are easy to sterilize or disinfect in order to ensure cross-infection control.
There is often a prism that allows splitting of the light beam in order that assistants may also visualize the procedure or to allow photography or video to be taken of the operating field.
OCT for Retina Scan and Glaucoma Scan
OCT
Optical Coherence Tomography is an imaging method used to generate a picture of the back of the eye, called THE RETINA. The picture is made by precisely measuring the amount of a dim red light that reflects off the retina. OCT is routinely used to image the eyes of patients with glaucoma and other retinal problems.
How OCT is done?
To prepare you for an Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) exam, your doctor may put dilating eye drops in your eyes in order to widen your pupil and make it easier to examine the retina. The patient simply looks into the lens of the device at a small, blinking target, the equipment scans the eye without touching it.

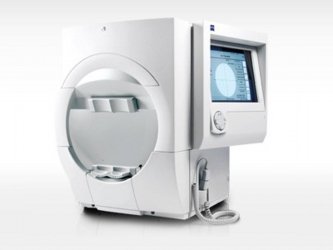
Perimetry
Humphrey field analyser (HFA)
Pachymetry
A pachymeter is a medical device used to measure the thickness of the cornea. It is used to perform corneal pachymetry prior to LASIK surgery, for Keratoconus screening, LRI surgery and is useful in screening for patients suspected of developing glaucoma among other uses.
HFA
Humphrey field analyser (HFA), is a tool for measuring the human visual field, it is used by optometrists, orthoptists and ophthalmologists, particularly for detecting monocular visual field. The results of the Analyser identify the type of vision defect.
What is the glaucoma Hemifield test?
The Glaucoma Hemifield Test compares points in the upper field to corresponding points in the lower field and then interprets the results as (a) “outside normal limits” indicating the upper and lower fields are different and may signify glaucoma, (b) borderline, and (c) within normal limits indicating glaucoma may not …
How do you detect glaucoma?
Regular eye examinations by your ophthalmologist (Doctor’s) are the best way to detect glaucoma. Your ophthalmologist will measure your eye pressure (tonometry); inspect the drainage angle of your eye (gonioscopy); evaluate your optic nerve (ophthalmoscopy); and test the visual field of each eye (perimetry).
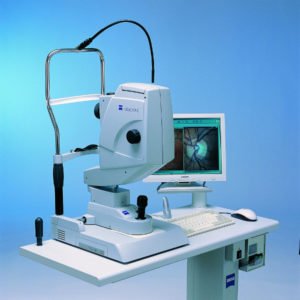
Fundus Camera & Angiography
Fundus Camera
A fundus camera is a specialized low power microscope with an attached camera. Its optical design is based on the indirect ophthalmoscope. Fundus cameras are described by the angle of view – the optical angle of acceptance of the lens.
FP
Where high-resolution images are required to be taken for diagnosing disorders in the retina, indirect ophthalmoscopy cannot be used. Instead, high-end benchtop devices exist (such as that shown on the right) which capture and record these images. These devices require the patient to be seated and to rest their chin on the device to keep their head in a fixed position relative to the device. A flash of light captures the image after proper alignment is achieved. This is called “fundus photography”.
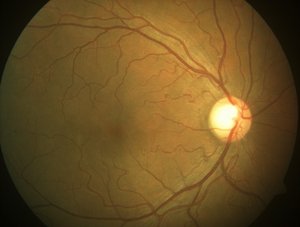
Normal Retina
On the left is a retinal (fundus) image of a normal healthy individual, taken using a high-end benchtop fundus imaging tool. Notice the bright white optic disk on the right, the blood vessels emanating from it (which supply blood to the retina) and the dark spot slightly off center, which is the fovea (responsible for central vision through which we do complex visual tasks like reading).
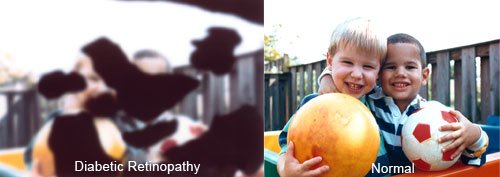
Diabetic retinopathy
On the right we have a fundus image of an individual suffering from Diabetic retinopathy. Notice the flaky white spots all over the retina. These “exudates” are deposits which causes “patches” to form in one’s vision. Diagnosing this condition is impossible without a good quality fundus imaging camera, which typically costs a few thousand dollars and is extremely large and heavy – definitely not a good solution for field screening programs.

How pt will See
What does this mean for the patient? Those small white spots lead to “blind spots” in one’s field of view. The image on the left simulates vision for someone suffering from this condition. If left unchecked, this can lead to permanent vision loss and the inability to perform routine tasks. India, where we are building this product, has the dubious reputation of being the diabetes capital of the world – about 63 million people suffer from diabetes, with this figure likely to go upto 80 million by 2025. About 37% of urban south asians suffer from diabetes or pre-diabetes and are at risk of developing DR. Timely treatment can reduce risks by more than 90%, however symptoms of vision loss only present themselves after significant progression of the disease.
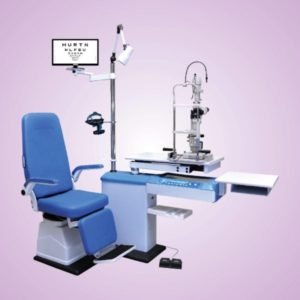
Slit Lamp Microscope
Slit Lamps utilize high quality optics, providing clarity and detail that will surprise even the most discriminating operator. The feather-touch XYZ joysticks, convenient controls, and ergonomic design, combined with top quality materials and meticulous assembly, ensure years of comfortable, enjoyable use. The outstanding optical performance, features and quality make series comparable to the world’s elite slit lamps.